Detect Brute-Force Attacks with nChronos Network Security Forensic Analysis Tool
 Brute-force attacks are commonly known attack methods by which hackers try to get access to restricted accounts and data using an exhaustive list/database of usernames and passwords. Brute-force attacks can be used, in theory, against almost any encrypted data.
Brute-force attacks are commonly known attack methods by which hackers try to get access to restricted accounts and data using an exhaustive list/database of usernames and passwords. Brute-force attacks can be used, in theory, against almost any encrypted data.
When it comes to user accounts (web based or system based), the first sign of a brute-force attack is when we see multiple attempts to login to an account, therefore allowing us to detect a brute-force attack by analyzing packets that contain such events. We’ll show you how Colasoft’s nChronos can be used to identify brute-force attacks, and obtain valuable information that can help discover the identity of the attacker plus more.
For an attacker to obtain access to a user account on a website via brute force, he is required to use the site’s login page, causing an alarming amount of login attempts from his IP address. nChronos is capable of capturing such events and triggering a transaction alarm, warning system administrators of brute-force attacks and when the triggering condition was met.
Visit our Network Protocol Analyzer Section for high-quality technical articles covering Wireshark topics, detecting and creating different type of network attacks plus many more great security articles.
Creating A Transaction Analysis & Alarm In nChronos
First, we need to create a transaction analysis to specify the pattern/behavior we are interested in monitoring:
From the nChronos main page, first select the server/IP address we want to monitor from the Server Explorer section.
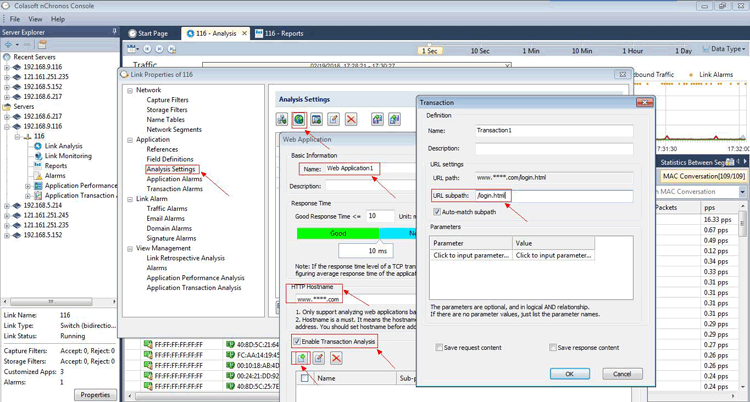
Next, from the Link Properties, go to the Application section and then the Analysis Settings as shown below:
Figure 1. Creating a Transaction Analysis in nChronos (click to enlarge)
Now click the button of New Web Application (second green button at the top) to set a Web Application, input Name and HTTP Hostname, then check the box labeled Enable Transaction Analysis and add a transaction with URL subpath e.g “/login.html”.
At this point we’ve created the necessary Transaction Analysis. All that’s required now is to create the Transaction Alarm.
To create the alarm, click Transaction Alarms in the left window, input the basic information and choose the parameter of Transaction Statistics in Type, and then set a Triggering Condition as needed, for example, 100 times in 1 minute. This means that the specific alarm will activate as soon as there are 100 or more logins within a minute:
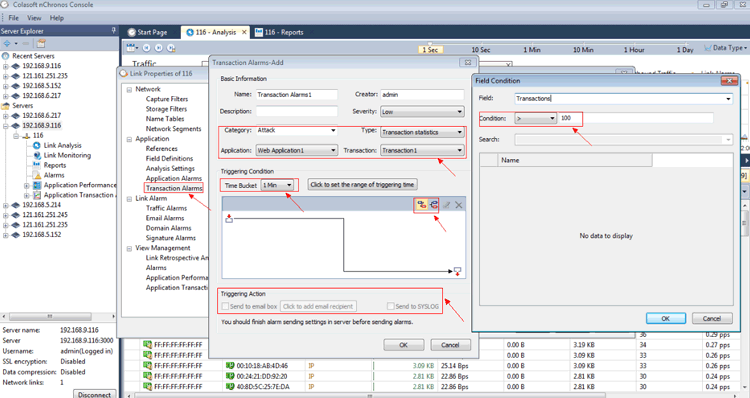 Figure 2. Creating a Transaction Alarm (click to enlarge)
Figure 2. Creating a Transaction Alarm (click to enlarge)
Finally, you can choose Send to email box or Send to SYSLOG to send the alarm notification. Once complete, the transaction alarm for detecting brute-force attack is set. When the alarm triggering condition is met an email notification is sent.
Note that the specific alarm triggering condition does not examine the amount of logins per IP address, which means the alarm condition will be met regardless if the 100 login attempts/min is from one or more individual IP addresses. This can be manually changed from the Transaction Analysis so that it shows the login attempt times of each individual IP address.
Below is a sample output from an alarm triggered:
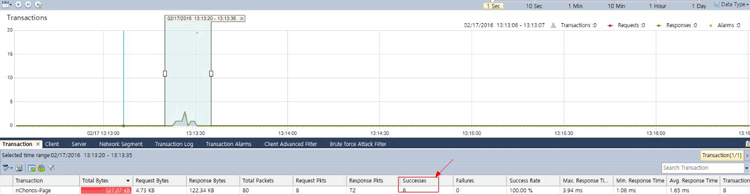 Figure 3. nChronos Brute-Force alarm triggered – Overall report (click to enlarge)
Figure 3. nChronos Brute-Force alarm triggered – Overall report (click to enlarge)
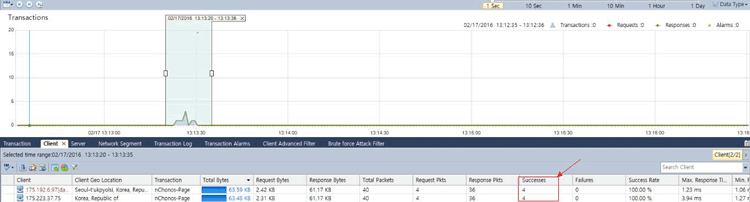
And below we see the same alarm with a per-IP address analysis:
Figure 4. nChronos Brute-Force alarm triggered – IP breakdown (click to enlarge)
The article shows how nChronos can be used to successfully detect a Brute-Force attack against any node on a network or even websites, and at the same time alert system administrators or IT managers of the event.
Your IP address:
3.145.133.121
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!