Hybrid Routing Protocols - Advantages and Disadvantages - Comparison
Hybrid routing protocols are a combination of distance-vector and link-state routing protocols, and are used to provide a more efficient and scalable routing solution in larger networks. These protocols are particularly useful in environments where there are multiple paths available between nodes, and the network topology is subject to change.
Article Key Topics:
- How do Hybrid Routing Protocol Work?
- Advantages of Hybrid routing protocols.
- Disadvantages of hybrid routing protocols.
- Examples of Hybrid routing protocols.
- Summary.
How do hybrid routing protocols work?
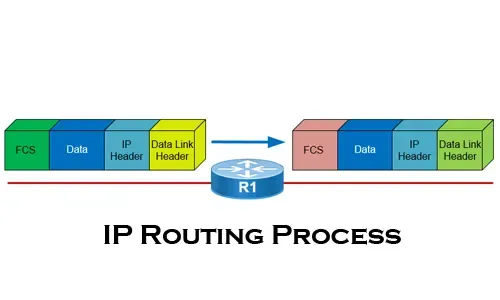
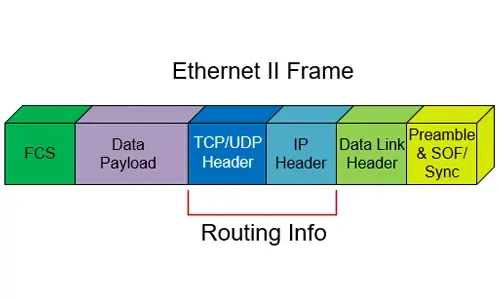
As mentioned earlier, Hybrid routing protocols use a combination of distance-vector and link-state routing protocols to provide a more efficient and scalable routing solution, while distance-vector routing protocols, such as Routing Information Protocol (RIP), work by exchanging routing information between neighbors, with each router broadcasting its entire routing table periodically. Link-state routing protocols, such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), work by distributing information about the state of links throughout the network, with routers constructing a complete map of the network topology.
Hybrid routing protocols combine the best features of these two protocols. They use distance-vector routing for small, stable networks, and link-state routing for large, complex networks with changing topologies.
Advantages of hybrid routing protocols
-
Scalability: Hybrid routing protocols are highly scalable and can handle networks with thousands of nodes. This is because they use link-state routing to provide a more accurate view of the network topology, and distance-vector routing to reduce the number of updates required.
-
Faster convergence: Hybrid routing protocols can converge quickly in the event of a network topology change, as they use both distance-vector and link-state routing to update routing tables.
-
Efficient use of bandwidth: Hybrid routing protocols use distance-vector routing to reduce the amount of bandwidth used for updates. Instead of broadcasting the entire routing table, routers only send updates for changed routes.
-
Load balancing: Hybrid routing protocols can distribute traffic across multiple paths, providing load balancing and increased network performance.
Disadvantages of hybrid routing protocols
-
Complexity: Hybrid routing protocols are more complex than either distance-vector or link-state routing protocols alone. This can make them difficult to configure and troubleshoot.
-
Resource-intensive: Hybrid routing protocols require more memory and processing power than distance-vector or link-state routing protocols alone.
-
Susceptible to routing loops: Hybrid routing protocols are susceptible to routing loops, which can occur when there are multiple paths between nodes and the routing protocol is not properly configured.
Examples of hybrid routing protocols
-
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP): EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary hybrid routing protocol that combines distance-vector and link-state routing. It uses a modified version of the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) to calculate routes and has several features that make it efficient and scalable, such as partial updates and route summarization.
-
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP): BGP is an exterior gateway protocol (EGP) used to route traffic between different autonomous systems (AS). It is a hybrid routing protocol that uses both distance-vector and path-vector routing to determine the best path for traffic.
Summary
Hybrid routing protocols are an effective solution for larger networks that require scalable and efficient routing. By combining distance-vector and link-state routing, hybrid routing protocols offer faster convergence, efficient use of bandwidth, load balancing, and scalability. However, they are also more complex and resource-intensive than either distance-vector or link-state routing protocols alone. Some examples of hybrid routing protocols include EIGRP and BGP.
Your IP address:
3.144.211.57
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!