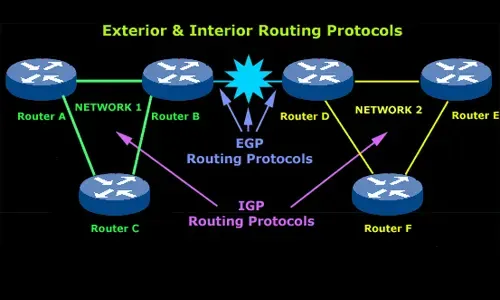
Routed Protocols
We all understand that TCP/IP, IPX-SPX are protocols which are used in a Local Area Network (LAN) so computers can communicate between with each other and with other computers on the Internet.
Chances are that in your LAN you are most probably running TCP/IP. This protocol is what we call a "routed" protocol. The term "routed" refers to something which can be passed on from one place (network) to another. In the example of TCP/IP, this is when you construct a data packet and send it across to another computer on the Internet
This ability to use TCP/IP to send data across networks and the Internet is the main reason it's so popular and dominant. If you're thinking also of NetBeui and IPx/SPX, then note that NetBeui is not a routed protocol, but IPX/SPX is! The reason for this is actually in the information a packet holds when it uses one of the protocols.
If you looked at a TCP/IP or IPX/SPX packet, you will notice that they both contain a "network" layer. For TCP/IP, this translates to the IP layer (Layer 3), as for IPX/SPX, it's the IPX layer (Layer 3). To make it easy to understand, I will use TCP/IP as an example.
In the picture below, you can see a TCP/IP packet within an Ethernet II Frame (The frame is like an "envelope" which encapsulates the TCP/IP packet):
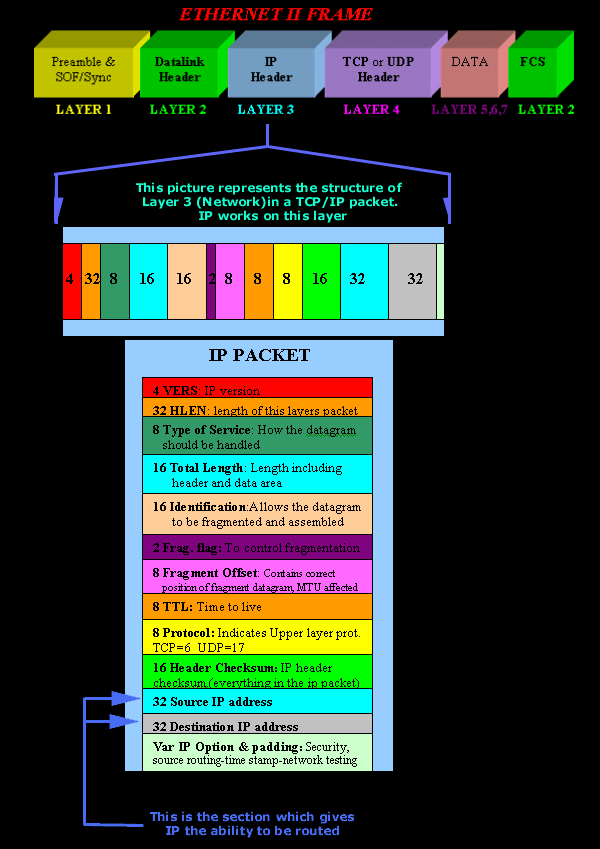
Looking closely, you will notice that Layer 3 (Network Layer) contains the IP header. It is within this section the computer puts the Source and Destination IP number. Thanks to the existence of this IP header, we are able to put a destination IP which can be one that's not on our network, and the computer will figure it out after completing a simple calculation and know if it needs to send this data to the router for it to be sent to its destination. You can read more on Layer 3 by visiting our OSI Model section.
IPX/SPX contains a similar field which gives it the same ability, which is to send packets over to different networks.
NetBEUI (NetBIOS Extended User Interface) on the other hand has no such information! This means that NetBeui has no information about the destination network to which it needs to send the data, as it was developed for LAN use only, or you could say that all hosts are considered to be on the same logical network and all resources are considered to be local. This classifies NetBeui as a "non routed" protocol.
Your IP address:
18.222.116.64
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!