Windows Server 2016 Licensing Made Easy – Understand Your Licensing Requirements & Different Server Editions
 This article describes the new Windows Server 2016 Licensing model (per-core licensing) Microsoft has implemented for its new server-based operating system. While the Windows Server 2012 Licensing model was fairly straight forward: per CPU Pair + CALS/DAL for Standard and Datacenter editions, Microsoft has decided to change its licensing arrangements thanks to the continuously increasing number of available cores per physical processor which has caused significant losses to its profits.
This article describes the new Windows Server 2016 Licensing model (per-core licensing) Microsoft has implemented for its new server-based operating system. While the Windows Server 2012 Licensing model was fairly straight forward: per CPU Pair + CALS/DAL for Standard and Datacenter editions, Microsoft has decided to change its licensing arrangements thanks to the continuously increasing number of available cores per physical processor which has caused significant losses to its profits.
Taking into consideration that the Intel Xeon E7-8890v4 contains a total of 24 cores capable of supporting up to 48 threads, one can quickly understand the software giant’s intention and why it is no longer continuing the per CPU Pair model for its Standard and Datacenter server editions.
Windows Server 2016 License Models
The Windows Server 2016 licensing model consists of per-core/processor + Client Access Licenses (CALs). Each user or device accessing a Windows Server Standard, Datacenter or Multipoint edition requires a Windows CAL or a Windows Server and a Remote Desktop Services (RDS) CAL.
In addition to these changes many would be surprised to know that there is now a minimum number of Per-Core licenses required per physical CPU and Server:
- A minimum of 8 core licenses is required for each physical CPU.
- A minimum of 16 core licenses is required for each server.
- A 2-core license pack is the minimum amount of core licenses you can purchase. E.g you’ll need four 2-core license packs (4x2) to fully license an 8-core CPU.
- The 2-core license is priced at 1/8 (one eighth) the price of a 2-CPU license for corresponding Windows 2012 R2 editions in order to keep the pricing similar. This means the pricing of a 16-core Windows 2016 Datacenter server is equal to a 2-CPU Windows 2012 R2 Datacenter server.
How Licensing Changes Affect Small Windows Server Deployments
Thankfully not much. Microsoft has adjusted its per-Core license pricing in such a way so that a small deployment of up to 16-cores per physical server will be the same pricing as a Windows server 2012 2-CPU License.
The price difference becomes apparent for larger customers with a server deployed that exceeds 8-cores per CPU and 16-cores per server. These customers will end up paying additional money for their licenses. For example a server with 2 x Intel Xeon E7-8890v4 CPUs means a total of 48 cores. Installing a Windows server 2012 Standard server means that the initial license will cover up to 16 out of the 48 cores and the customer will need to purchase additional licenses to cover the 32 extra cores! It’s now clear why big customers are going to be paying the big bucks!
The following table explains where additional licenses are required depending on the number of CPUs (processors) and cores per CPU. Remember - Minimum 8 cores/processor; 16 cores/server:
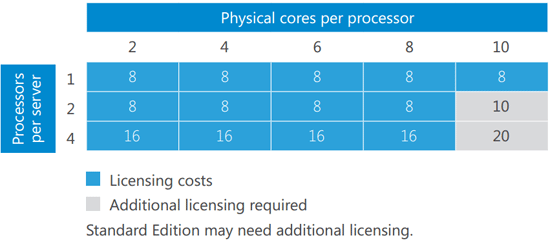
Figure 1. Windows Server 2016 Licensing: Calculating Licensing needs per CPU & Core
Windows Server 2016 Editions Overview, Licensing Models & CAL Requirements
Microsoft offers its Windows Server 2016 in 6 different editions. Let’s take a look at them and explain their primary role and usage:
Windows Server 2016 Datacenter: This edition targets highly virtualized datacenter and cloud environments. Main characteristics include its support for unlimited Hyper-V containers or Operating System Environments (OSEs or virtual machines). It also supports an unlimited number of Windows Server containers and boasts features such Host Guardian Service, Storage Spaces Direct and Storage Replica, Shielded Virtual Machines (VMs), Networking stack and more.
Windows Server 2016 Standard: Used for physical servers or environments with minimal virtualized requirements. This edition supports two Hyper-V containers or Operating System Environments (OSEs or virtual machines) alongside the Host Guardian Service.
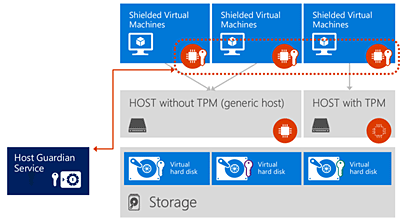
The Host Guardian Service is a server role introduced in Windows Server 2016 and found on Windows Datacenter and Standard edition. It serves as a critical security component in protecting the transport key, and works in conjunction with other Windows Server 2016 components to ensure high security levels for Shielded VMs.
Figure 2. Host Guardian Service helps ensure high security levels for Shielded VMs
Windows Server 2016 Essentials: Ideal for small businesses with no more than 25-30 users and 50 devices. This edition is also a great replacement for businesses running Windows Server 2012 Foundation as the same edition is not available for Windows Server 2016.
Windows Server 2016 MultiPoint Premium Server: Allows multiple users to share a single computer while having their own applications and Windows experience and is suitable for academic environments.
Windows Storage Server 2016: Suitable for dedicated storage solutions. It’s available in Standard and Workgroup editions and mainly used by OEM manufactureres.
Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016: The well-known Free Hypervisor which you can download. This is a stand-alone product that runs directly on the bare-metal server and is built using the same technology as the Hyper-V role on a Windows Server 2016.
The table below shows the licensing model adopted by each Windows Server 2016 edition:
|
Editions |
Licensing Model |
CAL Requirements |
|
Windows Server 2016 Datacenter |
Core-based |
Windows Server CAL |
|
Windows Server 2016 Standard |
Core-based |
Windows Server CAL |
|
Windows Server 2016 Essentials |
Processor-based |
No CAL Required |
|
Windows Server 2016 MultiPoint Premium |
Processor-based |
Windows Server CAL + Remote Desktop Services CAL |
|
Windows Storage Server 2016 |
Processor-based |
No CAL Required |
|
Hyper-V Server 2016 |
N/A |
N/A |
Table 1. Windows Server 2016 Editions and Licensing Models
Summary
With Windows Server 2016 out it’s only a matter of time before organizations begin to upgrade their servers and use it for new rollouts. Understanding the Windows Server 2016 Licensing model and server editions is critical to ensuring the right choices are made based on the organization’s requirements and server hardware availability. The new Windows Server core-based licensing can be slightly tricky so make sure you know your hardware and license theory well!
Your IP address:
18.227.190.93
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!