Ensuring Enterprise Network Readiness for Mobile Users – Wi-Fi, Bandwidth Monitoring, Shadow IT, Security, Alerts
 Demands for Enterprise networks to properly support mobile users is on a continuous rise making it more than ever necessary for IT departments to provide high-quality services to its users. This article covers 4 key-areas affecting mobile users and Enterprise networks: Wi-Fi coverage (signal strength – signal-to-noise ratio), Bandwidth Monitoring (Wi-Fi Links, Network Backbone, routers, congestion), Shadow IT (Usage of unauthorized apps) and security breaches.
Demands for Enterprise networks to properly support mobile users is on a continuous rise making it more than ever necessary for IT departments to provide high-quality services to its users. This article covers 4 key-areas affecting mobile users and Enterprise networks: Wi-Fi coverage (signal strength – signal-to-noise ratio), Bandwidth Monitoring (Wi-Fi Links, Network Backbone, routers, congestion), Shadow IT (Usage of unauthorized apps) and security breaches.
Today, users are no more tied to their desktops/laptops. Now, they are mobile. They can reply to important business emails, access their CRM, collaborate with peers, share files with each other & much more from cafeteria or car parking. This implies that it's high time for network admins at enterprises to think or give equal importance to wireless networks similar to wired networks. Wireless networks should be equally faster and secure.
Though the use of mobile devices for business actives is a good thing to happen for both enterprises and its customers, it also has some drawbacks on the network management side. The top 4 things to consider to make your network mobile ready are:
- Wi-Fi signal strength
- Bandwidth congestion
- Shadow IT
- Security breaches and attacks
 Figure 1. OpManager Network Management and Monitoring - Click for Free Download
Figure 1. OpManager Network Management and Monitoring - Click for Free Download
Wi-Fi Signal Strength
A good Wi-Fi signal is a must throughout the campus. Employees must not feel any connectivity problem or slowness because of poor signal quality. The signal should be so good and similar to the ones provided by the carriers. However, it’s not quite easy to maintain good signal strength all throughout the building. Apart from Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) and Wireless Access Point (WAP), channel interference also plays a major role in ensuring a good Wi-Fi signal strength.
RF interference is the noise or interference caused by other wireless & Bluetooth devices such as phones, mouse, remote controls, etc. that disrupts the Wi-Fi signal. Since all these devices operate on the same 2.4GHz to 5 GHz frequencies, it disrupts the Wi-Fi signal strength. When a client device receives another Wi-Fi signal it will defer transmission until the signal ceases. Interference that occurs during transmission also causes packet loss. As an effect Wi-Fi retransmissions take place which in fact slow down throughput and result in wildly fluctuating performance for all users sharing a given access point (AP).
Download your free copy of OpManager - Manage and Monitor your network
A common metric for measuring the Wi-Fi signal strength is the Signal-to-Noise (SNR) Ratio. SNR is the ratio of signal power to the noise power and expressed in decibels. SNR of 41db is considered excellent and 10-15db is considered as poor. However, as soon as interference is experienced SINR is the metric to look for. SINR is the Signal-to-Interference plus Noise Ratio which provides the difference between the signal level and the level of interference. Since RF interference creates disrupts the user throughput, SINR provides the real performance level of the Wi-Fi systems. A higher SINR is considered good as it indicates higher data rates.
 Figure 2. OpManager: Network Analysis – Alarms, Warnings and Statistics - Click for Free Download
Figure 2. OpManager: Network Analysis – Alarms, Warnings and Statistics - Click for Free Download
Shadow IT
Employees making use of third-party apps or services without the knowledge of IT, to get their job done is known as Shadow IT. Though it makes employees to choose the apps or services that works form them and be productive, it also leads to some conflicts and security issues. Using apps that are not verified by the IT team may cause serious security breaches and may even lead to loss of corporate data.
It's tough to restrict shadow IT because employees keep finding ways to find apps and services that they feel comfortable or easy-to-work with. And satisfied users use word-of-mouth marketing and increase the adoption of such apps/services among their peers. Sometimes, this creates conflict with existing IT policy and slows down the operations itself. However, the adoption of Shadow IT is on the rise. According to a study, shadow IT exists in more than 75% of the enterprises and expected to grow more.
Security Breach & Attacks
Public Wi-Fi hotspots are favorites for hackers. They try to steal data from the mobile devices that connect to the hotpots. Few years back The Guardian, a UK based journal deployed a mock Wi-Fi hotspot at an airport to demonstrate how critical information such as email ID, passwords, credit card data, etc. can be hacked via the Wi-Fi connection. Many travelers connected to hotspot and entered their details, which fraudsters could have misused in case of a real hack.
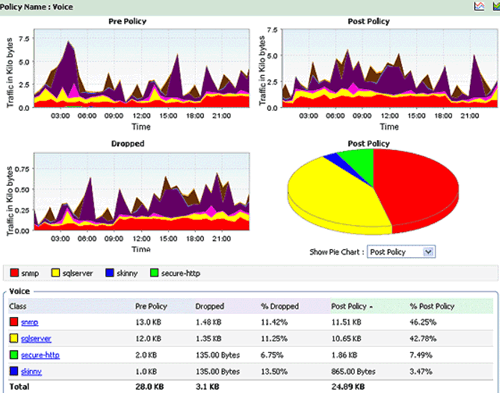 Figure 3. OpManager: Network Bandwidth, QoS and Policy Utilization - Click for Free Download
Figure 3. OpManager: Network Bandwidth, QoS and Policy Utilization - Click for Free Download
It's highly impossible for employees or as a matter of fact for anyone to refrain themselves from connecting to public Wi-Fi when they travelling or in public places. However, hackers use public Wi-Fi to inject malicious code that acts as Trojans, which in turn helps them steal corporate data.
Bandwidth Congestion
Admins have no control when it comes to employees accessing their mobile devices for their personal use also, which includes accessing sites such as Facebook, WhatsApp, YouTube, Twitter, etc. They cannot totally restrict them as the world is becoming more social, at least online, and have to allow them to use such apps. However, it should not take a toll on the employees accessing business critical apps.
Buying additional bandwidth is the usual approach followed to solve the bandwidth crisis. However, that’s not an effective way to manage bandwidth in enterprise networks. Most enterprises spend heavily on bandwidth. According to a survey done by us with the Cisco Live US, 2015 attendees, 52% of them spend more than $25,000 per month for bandwidth.
Effective Wireless Network Management Is The Need Of The Hour
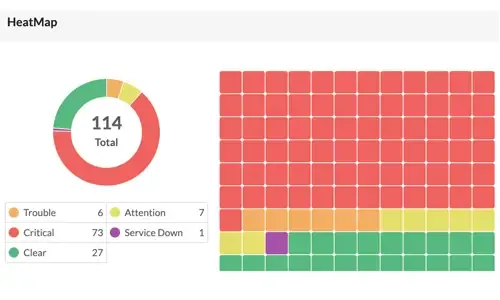
Wireless LAN Controllers (WLC) and Wireless Access Points (WAP) form the backbone of wireless network. It's very imperative to monitor them proactively so that any performance issues can be resolved before it turns big and impacts the users. Critical metrics such as SNR and SINR has also to be monitored in real-time so that any degradation in signal strength can be quickly identified and fixed. Heat-maps play a critical role in visually representing the signal strength across the floor. Make use of such heat maps and display it on the NOC screens so that any signal problem can be found out in real-time.
Having strict firewall and security policies combined with effective firewall management prevents enterprises from attacks and hacks caused due to hackers and shadow IT. For solving bandwidth related issues, network admins can make use of traffic shaping techniques to prioritize bandwidth for business critical apps. This avoids buying additional bandwidth often and helps providing adequate bandwidth for business critical apps and minimum bandwidth for non-business critical apps.
Doing all these manually would be highly cumbersome. Look out for tools or solutions that offer proactive monitoring of wireless networks, provide heat maps to identify and measure Wi-Fi signal strength, manage firewall configurations and policies, and troubleshoot bandwidth related issues. With such a solution and strict security policies in place, you can make your network ready for mobile devices.
ManageEngine OpManager is one such network management software that offers increased visibility and great control over your network. It out-of-the-box offers network monitoring, physical and virtual server monitoring, flow-based bandwidth analysis, firewall log analysis and archiving, configuration and change management, and IP address and switch port management, in one single exe. You can monitor WiFi signal strength
Your IP address:
18.216.194.71
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!