Statistics Highlight the State of Security of Web Applications - Many Still Vulnerable to Hacker Attacks
 Netsparker use open source web applications such as Twiki for a total different purpose than what they were intended for. They used them to test their own web application security scanners.
Netsparker use open source web applications such as Twiki for a total different purpose than what they were intended for. They used them to test their own web application security scanners.
Netsparker need to ensure that their scanners are able to crawl and identify attack surfaces on all sort of web applications, and identify as much vulnerabilities as possible. Hence they frequently scan open source web applications. They use open source web applications as a test bed for their crawling and scanning engine.
Thanks to such exercise Netsparker are also helping developers ship more secure code, since they report their findings to the developers and sometimes also help them remediate the issue. When such web application vulnerabilities are identified Netsparker release an advisory and between 2011 and 2014 Netsparker published 87 advisories.
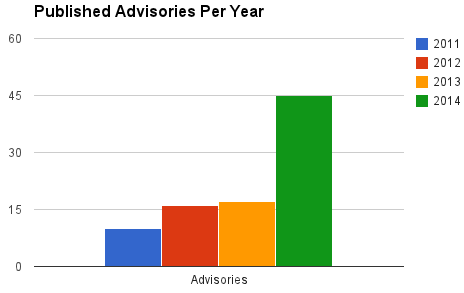
A few days ago Netsparker released some statistics about the 87 advisories they published so far. As a quick overview, from these statistics we can see that cross-site scripting is the most common vulnerability in the open source web applications that were scanned. Is it a coincidence? Not really.
The article also explains why most probably many web applications are vulnerable to this vulnerability, which made it to the OWASP Top 10 list ever since.
The conclusion we can draw up from such statistics is quite predictable, but at the same time shocking. There is still a very long way to go in web application security, i.e. web applications are still poorly coded, making them an easy target for malicious hacker attacks.
Your IP address:
18.217.244.16
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!













