Safety in Numbers - Cisco & Microsoft
By Campbell Taylor
Recently I attended a presentation by Lynx Technology in London . The presentation was about the complimentary use of Cisco and Microsoft technology for network security. The title of the presentation was “End-to-end SecurityBriefing” and it set out to show the need for security within the network as well as at the perimeter. This document is an overview of that presentation but focuses on some key areas rather than covering the entire presentation verbatim. The slides for the original presentation can be found at http://www.lynxtec.com/presentations/.
The presentation opened with a discussion about firewalls and recommended a dual firewall arrangement as being the most effective in many situations. Their dual firewall recommendation was a hardware firewall at the closest point to the Internet. For this they recommended Cisco's PIX firewall. The recommendation for the second firewall was an application firewall. such as Microsoft's Internet Security and Acceleration server (ISA) 2004 or Checkpoint's NG products.
The key point made here is that the hardware firewall will typically filter traffic from OSI levels 1 – 4 thus easing the workload on the 2nd firewall which will filter OSI levels 1 – 7.
To elaborate, the first firewall can check that packets are of the right type but cannot look at the payload that may be malicious, malformed HTTP requests, viruses, restricted content etc.
This level of inspection is possible with ISA.
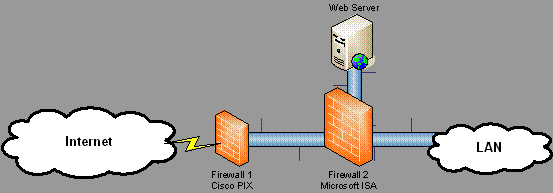 Figure 1. Dual firewall configuration
Figure 1. Dual firewall configuration
Provides improved performance and filtering for traffic from OSI levels 1 – 7.
You may also wish to consider terminating any VPN traffic at the firewall so that the traffic can be inspected prior to being passed through to the LAN. End to end encryption is creating security issues, as some firewalls are not able to inspect the encrypted traffic. This provides a tunnel for malicious users through the network firewall.
Content attacks were seen as an area of vulnerability, which highlights the need to scan the payload of packets. The presentation particularly made mention of attacks via SMTP and Outlook Web Access (OWA)
Network vendors are moving towards providing a security checklist that is applied when a machine connects to the network. Cisco's version is called Network Access Control (NAC) and Microsoft's is called Network Access Quarantine Control (NAQC) although another technology called Network Access Protection (NAP) is to be implemented in the future.
Previously NAP was to be a part of Server 2003 R2 (R2 due for release end of 2005). Microsoft and Cisco have agreed to develop their network access technologies in a complementary fashion so that they will integrate. Therefore clients connecting to the Cisco network will be checked for appropriate access policies based on Microsoft's Active Directory and Group Policy configuration.
The following is taken directly from the Microsoft website: http://www.microsoft.com/windowsserver2003/techinfo/overview/quarantine.mspx
Note: Network Access Quarantine Control is not the same as Network Access Protection, which is a new policy enforcement platform that is being considered for inclusion in Windows Server "Longhorn," the next version of the Windows Server operating system.
Network Access Quarantine Control only provides added protection for remote access connections. Network Access Protection provides added protection for virtual private network (VPN) connections, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) configuration, and Internet Protocol security (IPsec)-based communication.
ISA Server & Cisco Technologies
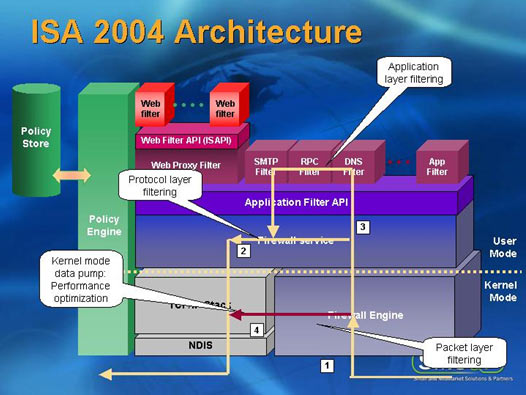
ISA 2004 sits in front of the server OS that hosts the application firewall and filters traffic as it enters the server from the NIC. Therefore intercepting it before it is passed up OSI levels.
This means that ISA can still offer a secure external facing application firewall even when the underlying OS may be unpatched and vulnerable. Lynx advised that ISA 2000 with a throughput of 282 Mbps beat the next closest rival that was Checkpoint. ISA 2004 offers an even higher throughput of 1.59 Gbps (Network Computing Magazine March 2003)
Cisco's NAC can be used to manage user nodes (desktops and laptops) connecting to your LAN. A part of Cisco's NAC is the Cisco Trust Agent which is a component that runs on the user node and talks to the AV server and RADIUS server. NAC targets the “branch office connecting to head office” scenario and supports AV vendor products from McAfee, Symantec and Trend. Phase 2 of Cisco's NAC will provide compliance checking and enforcement with Microsoft patching.
ISA can be utilized in these scenarios with any new connections being moved to a stub network. Checks are then run to make sure the user node meets the corporate requirements for AV, patching, authorisation etc. Compliance is enforced by NAC and NAQC/NAP. Once a connecting user node passes this security audit and any remedial actions are completed the user node is moved from the stub network into the LAN proper.
Moving inside the private network, the “Defence in depth” mantra was reiterated. A key point was to break up a flat network. For example clients should have little need to talk directly to each other, instead it should be more of a star topology with the servers in the centre and clients talking to the servers. This is where Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) would be suitable and this type of configuration makes it more difficult for network worms to spread.
Patch Management, Wireless & Security Tools
Patch Management
Patch management will ensure that known Microsoft vulnerabilities can be addressed (generally) by applying the relevant hot fix or service pack. Although not much detail was given Hot Fox Network Checker (Hfnetchk) was highlighted as an appropriate tool along with Microsoft Baseline Security Analyser (MBSA).
Restrict Software
Active Directory is also a key tool for administrators that manage user nodes running WXP and Windows 2000. With Group Policies for Active Directory you can prevent specified software from running on a Windows XP user node.
To do this use the “Software Restriction Policy”. You can then blacklist specific software based on any of the following:
- A hash value of the software
- A digital certificate for the software
- The path for to the executable
- Internet Zone rules
File, Folder and Share access
On the server all user access to files, folders and shares should be locked down via NTFS (requires Windows NT or higher). Use the concept of minimal necessary privilege.
User Node Connectivity
The firewall in Service Pack 2 for Windows XP (released 25 August 2004) can be used to limit what ports are open to incoming connections on the Windows XP user node.
Wireless
As wireless becomes more widely deployed and integrated more deeply in day-to-day operations we need to manage security and reliability. It is estimated Lynx that wireless installations can provide up to a 40% reduction in installation costs over standard fixed line installations. But wireless and the ubiquity of the web means that the network perimeter is now on the user node's desktop.
NAC and NAP, introduced earlier, will work with Extensible Authentication Protocol-Transport Level Security (EAP-TLS). EAP-TLS is used as a wireless authentication protocol. This means the wireless user node can still be managed for patching, AV and security compliance on the same basis as fixed line (e.g. Ethernet) connected user nodes.
EAP-TLS is scalable but requires Windows 2000 and Active Directory with Group Policy. To encrypt wireless traffic, 802.1x is recommended and if you wanted to investigate single sign on for your users across the domain then you could look at Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
As part of your network and security auditing you will want to check the wireless aspect and the netstumbler tool will run on a wireless client and report on any wireless networks that have sufficient strength to be picked up.
As a part of your physical security for wireless networking you should consider placing Wireless Access Points (WAPs) in locations that provide restricted user access, for example in the ceiling cavity. Of course you will need to ensure that ypu achieve the right balance of physical security and usability, making sure that the signal is still strong enough to be used.
Layer 8 of the OSI model
The user was jokingly referred to as being the eighth layer in the OSI model and it is here that social engineering and other non-technical reconnaissance and attack methods can be attempted. Kevin Mitnick has written “The Art Of Deception: Controlling The Human Element Of Security” which is highly regarded in the IT security environment.
One counter measure to employ for social engineering is ensuring that all physical material is disposed of securely. This includes internal phone lists, hard copy documents, software user manuals etc. User education is one of the most important actions so you could consider user friendly training with workshops and reminders (posters, email memo's, briefings) to create a security conscious work place.
Free Microsoft Security Tools
MBSA, mentioned earlier, helps audit the security configuration of a user/server node. Other free Microsoft tools are the Exchange Best Practice Analyser, SQL Best Practice Analyser and the Microsoft Audit Collection System.
For conducting event log analysis you could use the Windows Server 2003 Resource Kit tool called EventcombMT. User education can be enhanced with visual reminders like a login message or posters promoting password security.
For developing operational guidelines the IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL) provides a comprehensive and customisable solution. ITIL was developed by the UK government and is now used internationally. Microsoft's own framework, Microsoft Operations Framework draws from ITIL. There is also assistance in designing and maintaining a secure network provided free by Microsoft called “Security Operations Guide”
Summary
Overall then, the aim is to provide layers of defence. For this you could use a Cisco PIX as your hardware firewall (first firewall) with a Microsoft ISA 2004 as your application layer firewall (second firewall). You may also use additional ISA 2004's for internal firewalls to screen branch to Head Office traffic.
The user node will authenticate to the domain. Cisco NAC and Microsoft NAQC/NAP will provide a security audit, authentication and enforcement on these user nodes connecting to the LAN that gain authorisation. If any action is required to make the user node meet the specified corporate security policies this will be carried out by moving the user node to a restricted part of the network.
Once the user node is authenticated, authorised and compliant with the corporate security policy then it will be allowed to connect to its full, allowed rights as part of the Private network. If using wireless the EAP-TLS may be used for the authentication and 802.1x for the encryption of the wireless traffic.
To help strengthen the LAN if the outer perimeter is defeated you need to look at segmenting the network. This will help minimise or delay malicious and undesirable activity from spreading throughout your private network. VLANs will assist with creating workgroups based on job function, allowing you to restrict the scope of network access a user may have.
For example rather than any user being able to browse to the Payroll server you can use VLANs to restrict access to that server to only the HR department. Routers can help to minimise the spread of network worms and undesirable traffic by introducing Access Control Lists (ACLs).
To minimise the chance of “island hopping” where a compromised machine is used to target another machine, you should ensure that the OS of all clients and Servers are hardened as much as possible – remove unnecessary services, patch, remove default admin shares if not used and enforce complex passwords.
Also stop clients from having easy access to another client machine unless it is necessary. Instead build more secure client to server access. The server will typically have better security because it is part of a smaller group of machines, thus more manageable and its is also a more high profile machine.
Applications should be patched and counter measures put in place for known vulnerabilities. This includes Microsoft Exchange, SQL and IIS, which are high on a malicious hackers attack list. The data on the servers can then be secured using NTFS permissions to only permit those who are authorised to access the data in the manner you specify.
Overall the presentation showed me that a more integrated approach was being taken by vendors to Network security. Interoperability is going to be important to ensure the longevity of your solution but it is refreshing to see two large players in the IT industry like Cisco and Microsoft working together.
Your IP address:
3.14.7.99
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!













