What is a VPN? VPNs for Beginners - Everything You Need to Know About VPNs, Anonymous Browsing, Torrenting & VPN Security Features
What is a VPN?
 VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a well-known acronym amongst regular internet users. Initially used within businesses to securely connect to the corporate network, nowadays it’s being used by almost any type of user for anonymous browsing, protecting their privacy and stopping ISPs and government agencies tracking their online activities and transactions who are looking to capture users performing illegal file sharing of movies, music albums, torrenting or even trying to access geo-restricted content such as Netflix, Hulu and other streaming services.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a well-known acronym amongst regular internet users. Initially used within businesses to securely connect to the corporate network, nowadays it’s being used by almost any type of user for anonymous browsing, protecting their privacy and stopping ISPs and government agencies tracking their online activities and transactions who are looking to capture users performing illegal file sharing of movies, music albums, torrenting or even trying to access geo-restricted content such as Netflix, Hulu and other streaming services.
With the exponential rise of internet security threats it doesn’t really matter what type of device you’re using - whether it’s a PC, MAC, tablet, iPhone, Android device or smartphone - the risk is the same. Every single one of these devices can be tracked and their precise location known without any effort.
For example, the screenshot below was taken from a mobile phone. It shows a website visited that is able to track the mobile device’s IP address (49.185.251.16) and retrieve a significant amount of information regarding its location. It’s detected the country (Australia), the state (VIC), City (Melbourne), ISP/Mobile carrier (Optus) plus location and geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude)!
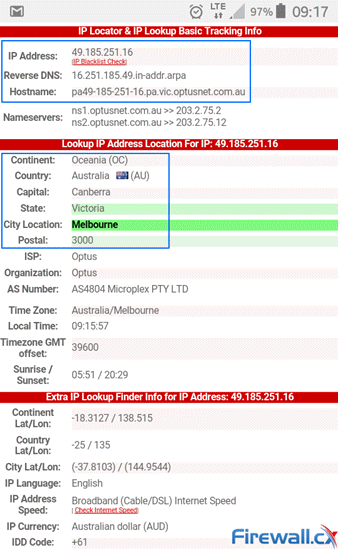
Information captured from a non-VPN internet user
As you can appreciate, the amount of information websites can capture is alarming. In a similar way ISPs, hackers and government agencies can intercept and capture traffic to and from a user’s mobile device or PC at home.
Now that we appreciate how exposed we really are, let’s take a look at how VPNs help protect our identity and personal information.
We highly recommend StrongVPN service provider - one of the worlds largest and most secure VPN providers.
Who Needs a VPN?
A VPN can offer a number of substantial advantages and, depending on your internet activities, can prove to be mandatory.
A VPN service will allow you to “hide” your physical location by masking the IP address assigned by your internet service provider (ISP). In addition, a VPN provides a basic level of security and confidentiality as all information to and from your computer or mobile device is encrypted. This prevents hackers or ISPs from monitoring your online activities.
Users typically require a VPN service for any of the following activities:
- Hide your internet activities from your ISP and government. ISPs around the world unofficially monitor user traffic in order to intercept sensitive or top secret information. More than 41 countries are now members of the “Five Eyes” – a global intelligence alliance monitoring electronic information (email, faxes, web traffic etc) and private communication channels (VPNs). The National Security Agency (NSA) was uncovered spying on hundreds and thousands of VPN connections based on Cisco’s PIX Firewalls for over a decade thanks to a VPN exploit they discovered and was never shared with the public.
- Accessing geo-restricted content. A prime explain is accessing US-based Netflix or Hulu when travelling overseas or accessing sites providing local online video/streaming, TV shows etc from anywhere around the world.
- Bypassing web filters and accessing restricted websites or internet services such as online gaming, Skype, Dropbox, OneDrive etc. Recent bans by governments blocking popular Torrent sites such as ThePiratebay.org, TorrentHound, Torrentz, IsoHunt and others have pushed users to VPN services in order to access these sites and services without restriction.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) file sharing. Usually blocked by firewalls or ISPs people are moving to VPN and ToR based networks in order to freely share data with each other without having to worry about being tracked or blocked.
- Torrenting. A big topic indeed. While there are many torrents that are legally distributed e.g Linux ISO images, open-source applications and games, Torrent seeders and leechers are monitored by agencies acting on behalf of their clients MPAA (Motion Picture Association of America) & RIAA (Recording Industry Association of America) to protect their copyright materials. While these agencies monitor and stop illegal video/music downloading they have been found on many occasions to incorrectly accuse citizens of illegally downloading copyright content.
- Avoid Bandwidth Throttling. ISPs are primarily responsible for this one. In order to save bandwidth they unofficially throttle torrent or other similar traffic, slowing download speeds considerably and sometimes to the point where users quit downloading. When it comes to VPN for Torrenting, P2P and File sharing users can avoid bandwidth throttling and in many cases increase their download speeds up to 3 times!
- Accessing the internet from public WiFi hotspots. Using Public WiFi and Guest WiFi hotspots poses serious security threats. These are overcome with the usage of VPN services.
The TOR network is an alternative VPN solution used also by the Dark-Web. Readers interested on how TOR VPN works and compares against VPN can also check our TOR vs VPN article.
Accessing The Internet Without a VPN
Below is a diagram showing a typical user accessing the internet without a VPN. The user’s IP address is assigned by the ISP and is visible to the internet. Any online resource accessed by the user is completely visible to the ISP and anyone monitoring the user’s IP address:
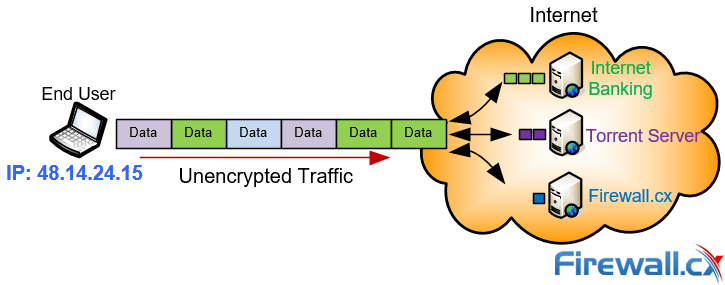
Unencrypted internet traffic is visible and easily monitored
Of course resources such as Internet Banking usually encrypt the data transferred between the client and the server but the traffic source (user IP) and destination (server IP) are still fully visible. Similarly other activities such as Torrent Downloads are fully traceable back to the user.
It should also be noted that ISPs always keep log files of their users’ IP addresses. This means that the ISP is fully aware of the IP address assigned to each of its users. By law, these logs are stored for years and can be used as evidence in the event of a law suit or investigation. This applies to home and mobile users.
Using a VPN Service Provider Changes The Game
To use a VPN service provider you must first register with a VPN Service Provider of your choice. VPN subscriptions start from a low $3US - $8US per month making them affordable for any user. Once you’ve purchased a VPN subscription you are able to download and install the provided VPN Client on to your devices.
With the VPN Client you are able to connect to one of your VPN Provider’s servers, which are located in various countries. Once connected, a “tunnel” is created between your device and the VPN server and all traffic is redirected to the VPN server and from there to the internet.
Any traffic traversing the tunnel is protected via special encryption mechanisms. Traffic entering the tunnel is encrypted while traffic exiting the tunnel is decrypted.
This means that anyone monitoring your internet connection e.g ISP, Hacker or Government agency, is unable to see your internet activities. All they can see is your encrypted traffic to the VPN server you’re connected to.

A VPN helps protect and encrypt all traffic to and from the internet avoiding any monitoring
When casually accessing websites or other online services it is unlikely they’ll be able to track your identity unless they require you to authenticate. For example if you need to access your Gmail account then you’ll need to provide your username and password. As that point your identity is known to Google even though you’re connecting via VPN, however, Google won’t be able to track your real location thanks to the VPN.
On the other hand if you are downloading a torrent file you don’t need to provide any credentials and therefore your identity remains hidden as long as you’re connected to the VPN.
To understand how well a VPN Service can disguise your activities, let’s go back to the initial example with the mobile phone and see how well a VPN Provider manages to hide a real IP address after connecting to a VPN server located in Canada:
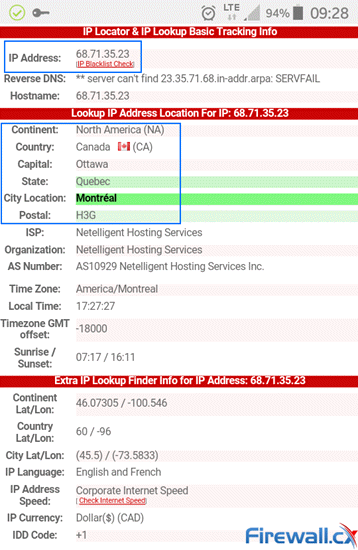
Changing locations. From Melbourne Australia to Canada thanks our VPN service
Notice how I’m now located in Canada and assigned a Canadian-based IP address. This is because our mobile’s internet traffic is tunnelled through the VPN all the way to the Canadian-based VPN server and exits from that point to the internet.
VPN Service Provider Shared IP vs Dedicated IP
When connecting to a VPN Service Provider you’ll usually be assigned a Shared IP address, that is, an IP address that is used by many users simultaneously. While using a Shared IP address might not sound ideal, it does in fact provide increased anonymity as opposed to using a Dedicated IP address that is solely assigned to your VPN account.
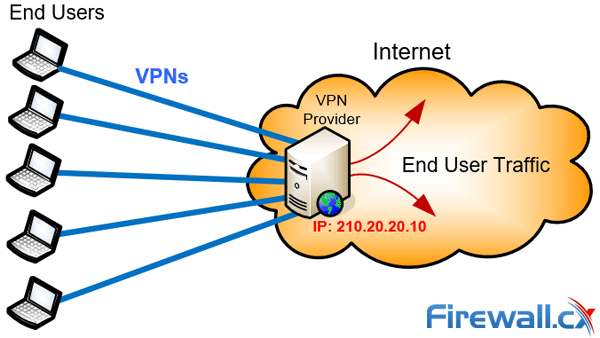
VPN Service Provider with Shared IP address
Dedicated IP addresses are usually required when accessing IP restricted servers or websites. Running a website or FTP server off your VPN Service Provider would also be a reason to make use of a Dedicated IP address.
For the majority of VPN users who perform casual web browsing, downloading, file sharing and require anonymous browsing capabilities the Shared IP address is considered a secure option.
Smart-DNS Proxy Server
Smart-DNS is a newer service provided by VPN Service Providers. Some offer it as an add-on service while others include it with the VPN subscription.
We’ve already explained that with a VPN service all internet traffic is channelled through an encrypted connection to a VPN server and exits to the internet from there.
With Smart-DNS a connection is established between the Smart-DNS server and client, however, communications are not encrypted and only selected traffic is channelled and sent to the Smart-DNS server, which works like a Proxy Server to help unlock access to geo-restricted services such as TV shows, NetFlix and other.
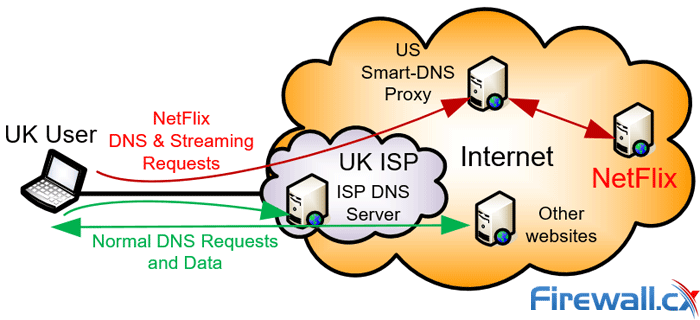
A Smart-DNS Proxy channels specific requests and data to unlock geo-restrictions
This is achieved by overriding selected DNS entries, e.g www.netflix.com, so that DNS queries resolve to the address of the Smart-DNS server rather than the real server. The Smart-DNS server accepts clients requests and acts as a proxy so that selected services are channelled through it, allowing access to any region-restricted or blocked content from anywhere in the world.
It’s important to keep in mind that Smart-DNS service is not a VPN Service replacement. All traffic sent and received via the Smart-DNS service is unencrypted and speeds are usually faster compared to a VPN thanks to the absence of encryption, making it an ideal solution for accessing region-restricted streaming services or services where data encryption is not important.
Impact Of a VPN On Your Mobile Device’s Speed, Battery Or Computer
Running a VPN connection will have an impact on your mobile device or computer. The level of impact will vary between different devices and their CPU processing capacity.
Following are key factors that will determine the impact on your device/system:
- CPU or processing power of your device (Single Core, Quad Core etc).
- Quality of the VPN Client software (poorly or well written software).
- VPN Encryption algorithm used to encrypt/decrypt data.
Let’s take a look at each point.
CPU – Processing Power Of Your Device
The faster the CPU the smaller the impact will be. Computers with iCore3, iCore5 or iCore7 processors offer more than enough power to perform all the necessary processing and a VPN will not significantly affect the user experience.
Mobile phones with dual or quad CPU should also be able to handle a lightweight VPN Client without any difficulty, however, you must keep in mind that heavy internet usage also means more work for the CPU – this translates to a battery that is drained at a much faster rate. Mobile users should generally use the internet in the same way as before installing the VPN client to see the real impact it will have on their device. Newer mobile devices shouldn’t experience any noticeable difference.
Quality Of The VPN Client Software
Just like any piece of software a well-designed VPN application will function without problems and will limit its usage of system resources. There are VPN Providers that offer very cheap subscriptions, however, their VPN Client software might be buggy causing either frequent crashes or taking a long time to respond to user actions.
It’s recommended to make use of high-quality VPN providers such as StrongVPN and ExpressVPN who develop and thoroughly test their software. Our Best VPN review offers a comparison between 5 Top VPN Services for you to choose from.
VPN Encryption Algorithm
There are quite a few VPN encryption options available through your VPN Client and each one of these will provide you with a different level of security. Stronger encryption, e.g. L2/IPSec, means better security, however, this will have a slightly larger toll on your device’s CPU as it will be required to work harder to encrypt and decrypt your traffic due to the high complexity of the strong encryption protocols.
On the other hand, selecting a weaker encryption protocol such as PPTP means that demands on the CPU will be lower but so will the security offered.
Newer protocols, such as OpenVPN, combine the best of both worlds and deliver a fast & secure VPN service at minimal cost to your CPU. OpenVPN is generally the recommended VPN protocol.
VPN Protocols
As mentioned earlier a VPN makes use of different encryption protocols to secure the connection between the end-user and the VPN server. Selecting the best VPN protocol is important so let’s discover the most commonly supported encryption protocols used by VPN providers:
- PPTP - Point to Point Tunnel Protocol. Old lightweight VPN protocol which is still very popular but doesn’t offer much security. Ideal for streaming and basic VPN needs but not for torrenting.
- L2TP / IPSec - Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol & IP Security. The evolution of PPTP offering much better security and encryption at the slight expense of speed.
- SSTP - Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol. A flexible SSL-based encryption by Microsoft. Good alternative to L2TP/IPSec but not as good as OpenVPN.
- OpenVPN – a newer open-source VPN protocol that offers great security, flexibility and compatibility. Supported by router firmware such as DD-WRT, Tomato and others.
- More servers means better VPN user distribution. This translates to faster servers and fewer users per VPN server.
- Higher service availability. If one or many servers go down you’ll have plenty of others to connect to therefore limiting the impact on your VPN service.
- Ability to access geo-restricted content for every country that has a VPN server available for you to connect to.
- Ability to connect to a VPN server that is located closer to the source you are trying to access, therefore providing better download/upload speeds.
Users should be aware that not all encryption protocols offer the same security and performance level. For example, PPTP is an older VPN protocol that doesn’t really encrypt the information but simply encapsulates user’s data. Think of it as placing a letter (data) inside a standard envelope. The envelope is light so you can carry more of them within a specific period (high performance / throughput). Despite the lower security offered by PPTP, it is still widely used today because not many understand the level of security it provides but also because it’s managed to penetrate the market the past 15 years and is still supported by newer VPN devices and servers.
On the other hand L2TP/ IPSec is the evolution of PPTP and was introduced as an alternative more-secure VPN protocol. It offers significantly higher security but is a slower protocol meaning it has more overhead.
SSTP is a Microsoft proprietary protocol found on all Windows operating systems after Windows Vista Service Pack 1. SSTP is preferred over PPTP and L2TP as it is able to pass through most firewalls without a problem (requires TCP Port 443) whereas PPTP and L2TP/IPSec might not be able to pass through a firewall as they use uncommon TCP/UDP ports which are usually blocked by corporate or guest networks.
Finally, OpenVPN is by far the preferred VPN protocol. It’s an open-source (freely distributed) newer technology supported almost every device and VPN service provider. It’s flexible, offers great security, has moderate CPU demands and will run in almost any environment capable of passing through firewalls without a problem. In addition, router software such as DD-WRT, Tomato and Mikrotik support OpenVPN allowing users to connect to their VPN provider at the router level, removing the need for any VPN client software on devices connecting to the home or business network.
Using the right VPN encryption protocol is important as it will significantly affect the security provided as well as your upload/download speeds.
VPN Servers – The More – The Merrier
VPN Service Providers generally deploy VPN servers around the globe to accommodate their customers. Using a VPN Provider that has hundreds or thousands of servers deployed is always a great option and there are plenty of reasons for this:
- More servers means better VPN user distribution. This translates to faster servers and fewer users per VPN server.
- Higher service availability. If one or many servers go down you’ll have plenty of others to connect to therefore limiting the impact on your VPN service.
- Ability to access geo-restricted content for every country that has a VPN server available for you to connect to.
- Ability to connect to a VPN server that is located closer to the source you are trying to access, therefore providing better download/upload speeds.
If the VPN Provider does not reveal the number of VPN servers it maintains, then check the list of countries and cities where VPN servers are available – this information is usually provided and is a good indication that there are plenty of servers to select from.
VPN Kill-Switch Feature – Avoid Accidently Exposing Your Identity
The VPN Kill-Switch is a feature built into the VPN Client so that when enabled it will continuously monitor your VPN ensuring all traffic is passing through the VPN.
When the Kill-Switch detects that your VPN has disconnected it will automatically stop all internet traffic from and to your PC or mobile device to avoid it from exposing its real identity - IP address.
A VPN with the Kill-Switch enabled is the best practice for torrenting as it helps users from accidently exposing themselves to the public, especially when torrenting over night or the PC is left switched on to complete its download(s).
DNS Leak Protection
When connecting to a VPN the PC or mobile device is forced to use secure DNS servers for all DNS queries. These DNS servers are usually the VPN provider’s DNS servers. This ensures the ISP and government is unable to track any DNS queries which might reveal the user’s online activities.
A DNS Leak occurs when the operating system begins sending DNS queries to the ISP’s DNS or other insecure DNS servers. The reason for a DNS leak might be intentionally modified device settings (e.g DNS server settings) or even the way the operating system behaves – which is the case with the Windows operating system.
One of Windows 10 new features allows it to direct DNS requests to the local network router or ISP, bypassing the VPN tunnel. This setting was designed to enhance and speed-up the DNS query process however it has created a major security issue as users can easily be exposed without knowning.
Our DNS Leak Testing & Protection article explains the problem in-depth and provides ways to protect against it. A high-quality VPN service will include DNS leak protection embedded within the VPN client to help protect its users from being unknowingly exposed to this serious security threat.
‘No-Log’ VPN Service Provider Policy
Not all VPN Service Providers are completely anonymous. Some VPN Service Providers keep extensive logs of their users’ IP addresses and VPN login sessions.
A ‘no-log’ VPN Service does not keep any logs of its users or their online activities therefore making it extremely difficult to trace any of their online activities.
VPN Providers that keep some type of logs seriously risk exposing their users. In the event of a security breach, or government demand to access these logs, users are left vulnerable as it will make it easier to trace previous online activities.
VPN Service Providers who offer a “no log” policy usually state something along the following lines in their privacy policy:
“We never keep traffic logs, and we also don’t keep any logs that might enable someone to match an IP and timestamp back to a user.”
It’s important to keep in mind that depending on the country where the VPN Provider resides, they might be required by law to store their logs no matter what impression they give on their site. For example, countries such as Romania, Netherlands, Sweden and Luxembourg are not currently required to keep logs while other countries in the European Union are required to do so.
Make sure the VPN provider’s “no log” policy is absolutely clear to you before signing up.
Paying your VPN Service Provider without Exposing Your Identity
VPN Service providers accept a number of different methods including credit cards, VISA, MasterCard, PayPal, BitCoin and more.
While users can use any of the above methods for payment those concerned sharing personal information and seeking complete privacy can use BitCoin.
BitCoin is a virtual form of digital currency that allows users and companies to transact online without going through a bank. Payments are anonymous so there is no trace of your identity and since banks are not involved in the transaction there are fewer fees both for the sending and receiving party.
Money-Back Guarantee – Making the Most Out of Your Trial
The money-back guarantee option is usually offered by the popular and reputable VPN Service Providers. Some offer a 3, 5, 7 or 30 day refund policy while others provide a free usage period after which you are required to purchase a subscription if you wish continue using the service.
Whichever the case, a “try before you buy” policy is always preferred since it provides you with the opportunity to try the service and ensure it works well for you. It is always recommended when trying a new VPN service to connect to multiple VPN servers throughout the trial period to help get a good idea on how well the VPN provider is performing. Try downloading via Torrent, accessing Netflix or similar services, visit frequently used websites and see how the service performs before commit to a long-term plan.
Finally ensure you are fully aware of the money-back guarantee conditions. Some VPN providers will happily provide a refund within the trial-period however they might refuse to issue the refund in case of excessive downloads.
Number of Simultaneous VPN Connections
All VPN Service Providers support simultaneous connections using a single VPN account allowing users with multiple devices e.g laptop, mobile phone, tablet etc, connect through any of their devices.
Users who wish to take advantage of a VPN Service will surely appreciate this capability and it’s quickly becoming very popular. Many users take advantage of this feature and share the VPN account with friend to split the VPN cost.
A minimum of at least 2 simultaneous VPN connections should be supported by your provider, one for the laptop/workstation and one for your mobile phone or tablet. Support for more than 2 devices is always nice to have as you can easily share it with a friend.
Customer Support
VPNs have evolved enough today so that a user at any technical level should be able to download and install the VPN Client without difficulties. Nevertheless, if you’re new to VPNs the amount of information can often be overwhelming and confusing.
For this reason 24/7 Customer Support is important and it should be easily accessible via the provider’s website, email or even phone.
The most common method today is 24/7 online chat support followed by email support while some providers might even offer phone support.
With chat and email support you should be able to precisely describe any problem you are having so that the person on the other side can understand. This will help resolve your problem much faster and save time and unnecessary frustration.
Choosing the Right VPN Provider
With over 200 VPN Service Providers, making the right choice can be a very complicated and time-consuming task. While the price tag always plays a significant role it should not be the major decision-making factor.
Protecting your online privacy correctly is very important even if that means spending a few additional dollars.
Firewall.cx is the only network security site with industry security experts who have performed in-depth reviews of VPN providers to produce the Best VPN Service guide based on the following criteria:
- VPN Speeds and Latency Test
- VPN Server locations (countries) amount of servers world-wide
- Netflix VPN, Torrenting and Blocked sites, Geo-blocking Bypass
- Security features (DNS Leak Protection, Kill Switch etc)
- Multiple device login (Laptop, Phone, Tablet etc)
- Encryption protocols (PPTP/L2TP IPSec/OpenVPN etc) & Support for Dedicated VPN Routers
- No-Log Policy & Bitcoin payment support
- User-Friendly VPN client interface
- Pricing – based on a 12 month subscription
Summary
Understanding what a VPN service is and how it can help you protect your online privacy is very important today. Enabling anonymous browsing and protecting your online identity against attack is as equally important as running an antivirus on your computer. VPN Services help provide a significant level of identity protection while at the same time unlocking geo-restricted content with the click of a button. Protect your online transactions and activities with a highly recommended VPN Service today.
Your IP address:
3.145.15.34
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!













