IP Protocol - Part 2: The Internet Protocol (IP) Header
This article examines the Internet Protocol (IP) and its position within the OSI Model. We take a look at the IP Header and all fields contained within an Ethernet frame. Further examination of the IP header is covered in the next pages that follow.
Just like every other protocol, the Internet Protocol has a place in the OSI Model. Because it's such an important protocol and other protocols depend upon it, it needs to be placed before them, which is why you will find it in Layer 3 of the OSI model:
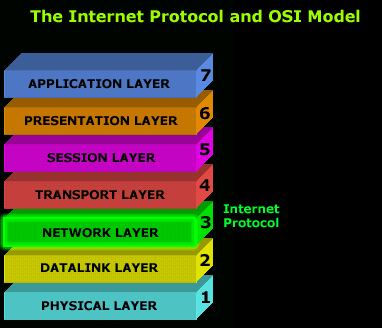
When a computer receives a packet from the network, the computer will firstly check the destination MAC address of the packet at the Datalink layer (2) and if it passes, it's then passed on to the Network layer
At the Network layer it will check the packet to see if the destination IP Address matches with the computer's IP Address (if the packet is a broadcast, it will pass the network layer anyway).
From there, the packet is processed as required by the upper layers.
On the other hand, if the computer is generating a packet to send to the network then, as the packet travels down the OSI model and reaches the Network layer, the destination and source IP Address of this packet are added in the IP Header.
The IP Header
Now we are going to analyse the Internet Protocol header, so you can see the fields it has and where they are placed. In here you will find the destination and source IP Address field which is essential to every packet using the protocol.

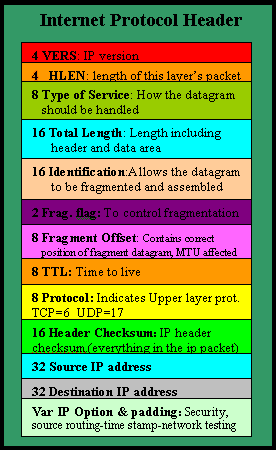
It's worth noting that the 9th field, which is the "Protocol" field, contains some important information that the computer uses to find out where it must pass the datagram once it strips off the IP header.
If you remember, TCP and UDP exist on layer 4 of the OSI Model, which is the transport layer. When data arrives at a computer and the packet is processed by each layer, it needs to know whereabouts above to pass the data. This protocol field tells the computer to give the remaining data to either the TCP or UDP protocol, which is directly above it.
Also, the Destination IP Address is another important field which contains the IP Address of the destination machine.
The next section talks about the 5 different classes of IP Address.
Your IP address:
3.144.115.125
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!















