Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol - EIGRP
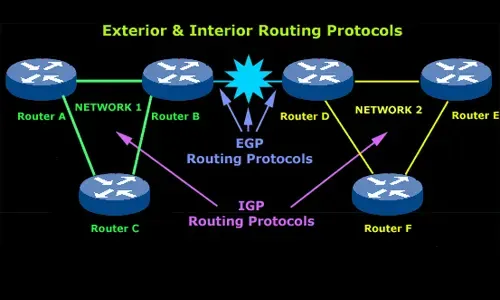
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), similar to IGRP, is a Cisco proprietary routing protocol that is used to exchange routing information between different routers within a network. EIGRP is an advanced routing protocol that combines the features of both distance vector and link-state routing protocols. This protocol is used to provide faster convergence times and improved scalability. EIGRP uses a composite metric composed of Bandwidth, Delay, Reliability, and Loading to determine the best path between two locations.
Article Key Topics:
- Key Points of EIGRP.
- Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL).
- EIGRP and Multicast.
- Classless Operation.
- EIGRP Limitations.
Key Points of EIGRP
-
Fast convergence times: EIGRP has a fast convergence time, which means that it can quickly adapt to changes in the network topology.
-
Loop-free paths: EIGRP provides loop-free paths. This helps prevent routing loops and ensures the integrity and convergence stability of the network.
-
Support for VLSM: EIGRP supports variable length subnet masks (VLSM), therefore allowing for more efficient use of IP address space.
-
Scalability: EIGRP can scale to support almost any size network but is usually found in small to large networks.
Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL)
The Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) is the core of EIGRP's operation. DUAL is responsible for calculating the shortest path to a network destination and for selecting the best path among multiple paths. DUAL is also responsible for providing loop-free paths, reducing network convergence times, and minimizing the use of network bandwidth.
DUAL uses three tables: the neighbor table, the topology table, and the routing table. The neighbor table keeps track of neighboring routers, the topology table contains information about network topology, and the routing table contains the best paths to network destinations.
EIGRP and Multicast
EIGRP uses multicast addresses to distribute routing updates and queries to its neighboring routers. The multicast address used by EIGRP is 224.0.0.10. This address is used by EIGRP routers to send hello messages to each other and also to send updates and queries to their neighbors.
When a router sends a multicast update to its neighbors, it includes only the routes that have changed since the last update. This helps to reduce the amount of traffic on the network and also reduces the processing power required by the routers. EIGRP also supports incremental updates, which means that only the changes to the routing table are sent, not the entire routing table.
EIGRP's use of multicast communication is also advantageous because it enables routers to discover new neighbors quickly. When a router sends a hello message to the multicast address, any neighboring routers that receive it will respond with their own hello messages. This allows routers to quickly learn about the topology of the network and update their routing tables accordingly.
However, there are some potential limitations to using multicast communication with EIGRP. One potential issue is that the multicast packets can be dropped or delayed on networks with high congestion. Additionally, if there are any network segments that do not support multicast communication, EIGRP may not be able to communicate with routers on those segments.
Despite these potential limitations, EIGRP's use of multicast communication remains a powerful tool for efficiently sharing routing information in large networks. By using a combination of distance-vector and link-state technologies, EIGRP is able to provide fast convergence times and efficient use of network resources.
Classless Operation
EIGRP is a classless routing protocol. This means that it supports variable length subnet masks (VLSM), which means it includes subnet mask information in its routing updates and enables network administrators to use subnets of different sizes within a network. This allows for more efficient use of IP address space.
Since an EIGRP update it includes the IP address of the destination network along with its, it enables the receiving routers to calculate the correct network address and determine the length of the prefix for the network, allowing them to support VLSMs.
In addition to supporting VLSMs, EIGRP also supports automatic summarization of routes at network boundaries. This means that EIGRP routers will automatically summarize the routes within their own networks and advertise the summary to neighboring routers. This reduces the amount of routing information that needs to be transmitted across the network and improves network efficiency.
However, there are some potential disadvantages to using classless operation with EIGRP. One potential issue is that it can increase the complexity of network designs and configurations. Additionally, classless operation can also increase the size of routing tables, which can impact the performance of routers with limited memory or processing power.
Despite these potential challenges, EIGRP's support for classless operation remains a valuable feature that enables network administrators to create more efficient and flexible network designs. By using VLSMs and automatic summarization, EIGRP is able to provide more granular control over network subnets and reduce the amount of routing traffic on the network.
EIGRP Limitations
One of the main limitations of EIGRP is that it is a proprietary protocol that is only supported by Cisco networking equipment. This means that it cannot be used in networks that include non-Cisco devices, and can limit the ability to interoperate with other routing protocols.
Another limitation of EIGRP is that it requires a certain amount of resources to operate efficiently. Specifically, EIGRP requires a significant amount of CPU and memory resources to calculate and maintain its routing tables. As a result, it may not be the best choice for networks with limited resources or older equipment.
EIGRP also has limitations when it comes to scalability. While EIGRP can scale well within an autonomous system (AS), it may not be the best choice for very large networks or networks with many ASs. In these cases, other routing protocols like OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) may be a better choice.
Finally, EIGRP's default metrics may not always be the most appropriate for certain types of networks or traffic patterns. While EIGRP allows for the tuning of its metrics, this can be a complex and time-consuming process, and may not always result in optimal performance.
Despite these limitations, EIGRP remains a popular and effective routing protocol in many networks, especially those that are primarily composed of Cisco equipment. However, network administrators should carefully evaluate the specific needs and limitations of their networks before selecting EIGRP as their routing protocol of choice.
EIGRP Disadvantages
-
Proprietary protocol: EIGRP is a proprietary protocol, which means that it is only supported on Cisco routers.
-
Limited support for non-Cisco devices: EIGRP has limited support for non-Cisco devices, which makes it difficult to use in heterogeneous network environments.
Summary
EIGRP is an advanced Cisco proprietary routing protocol that combines the features of both distance vector and link-state routing protocols. EIGRP uses the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) to provide loop-free paths, fast convergence times, and scalability. EIGRP uses multicast to distribute routing updates, which reduces network traffic and improves scalability. EIGRP is a classless routing protocol that supports VLSM.
Your IP address:
3.22.208.99
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!